Log Operations Panel
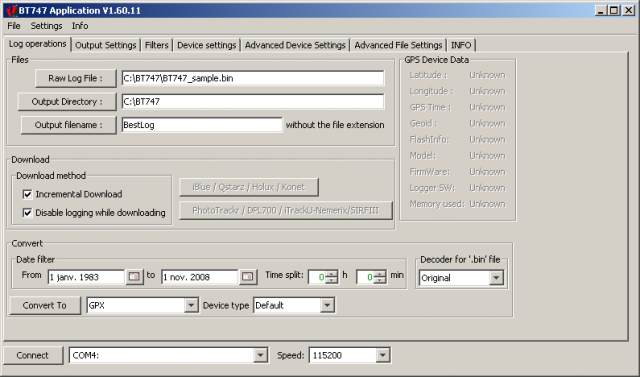
| Connect Shown on all screens! |
|
|---|---|
| Connect button: | Click to connect to the indicated serial port. Once connected, this button will change into 'Disconnect' and can be used to stop the connection to the device. |
| Port name: | Select the system port that interfaces with the GPS device. It is possible to type the port name directly - it does not have to be in the list. "USB" will attempt to locate the USB port automatically on Linux and MacOSX systems. "BLUETOOTH" will try to locate the bluetooth port automatically on MacOSX systems. |
| Speed: | The speed to use for the serial connection. Most of the time 115200 baud will be the correct speed, in some cases 38400 baud is needed (this is the case for the Holux M-241). If the speed is not in the list, you can enter the speed directly. |
| Files | |
| Raw Log File: |
The file to which the data is saved when downloading, or read when converting. The extension should be '.bin', except for Phototrackr and similar devices where it should be '.sr'. it is important that the extension is '.bin' for raw log formats! |
| Output Directory: | Location where the files created during conversion will be written. |
| Output filename: |
The basename of the files that will be written. This does not include the filename extension. The path is relative to the output directory. The basename will be post-fixed with date and time information as well as the appropriate file extension for the chosen output format. It is possible to have a customised based name by using '%*' tokens. Please see http://php.net/manual/en/function.date.php for details - most of the 'php' formatting options are available. As soon as you specify a '%' token in your filename, BT747 will no longer do its magic and you assume the entire responsibility that the resulting filename is unique (for instance, if you have more than one file for the same day, make sure that you include the hour and minutes - not just the day). |
| Download | |
| Incremental Download: | If data was previously downloaded to the device in the file specified as Raw Log File and the data in the Raw Log Files looks the same as the one currently present in the Device, only new data will be downloaded. This will speed up the download substantially. If the data is different, the user will be requested to confirm overwriting the data. |
| Disable logging while downloading: | Normally the device will continue logging regardless of wheter a download is going on. To avoid filling the memory while you are downloading, tick this option and the device will be instructed to stop logging. At the end of the download the logging will be activated again if it was active at the start of the download. |
| iBlue / Qstarz / Holux / Konet: | Download from this type of device. This is valid in most cases. |
| PhotoTrackr / ...: | Download from one of these devices. The download protocol and format is different. This is currently experimental as no user actually confirmed correct operation. |
| Convert | |
| From ... To ...: | The date range for the records to be converted. This is a filter, but it something the user may want to configure every time. Therefore it is located in the main panel. |
| Time split: | This time will be used as the start time on the indicated 'from' day (taking into account the UTC offset in the 'Output Settings' panel and as the end time on the day following the indicated 'end day'. For instance, if you filter from September 2nd to November 1st, and the time is 2h30min, the chosen records will be between September 2nd at 2h30 and November 2nd at 2h30. |
| Decoder for bin file: | A user developed an alternative decoder for raw binary files. That one is still buggy but kept availalbe for testing, so you'ld better choose the 'Original'. |
| GPS Device Data Live position data from the GPS device. |
|
| Latitude: | Latitude of the current position. |
| Longitude: | Longitude of the current position. |
| GPS Time: | GPS time (UTC reference) returned by the device. |
| Geoid: | The offset of the Geoid (or Mean Sea Level) to the WGS84 elipsoid. Both are model of the earth 'surface'. In its NMEA packets, the GPS provides the Geoid offset versus the WGS84 and also the altitude of the position versus the Geoid. The GPS device calculates the Geoid itself - the actual reference is the WGS84. In the log the 'height' or 'altitude' that is logged is the WGS84. BT747 calculates the Geoid for itself, and that value is indicated here too to see if this corresponds with the device's calculation (which is a bit less precise). |
| Flashinfo: | The flash ID (a hexadecimal value that can be used to identify the flash type) and an interpretation of it: manufacturer and size in bytes (not bits). When the manufacturer reports 16Mb, BT747 reports 2MB. The first value is Megabits, the latter one Megabytes! |
| Model: | Shows the model ID number as returned by the device. In parentheses is the guessed device name. |
| Firmware: | Firmware version information as returned by the device. Some devices return very long information and then this information is split on two lines. If the first line ends with '...', use the tooltip text to see the entire string. |
| Memory used: | The number of bytes filled in the log memory. In parentheses the percentage of memory filled. |
- Druckversion
- Anmelden um Kommentare zu schreiben
- Deutsch
Kommentare
Three download modes
Using Holux M-241 with BT747 V2.0.3
What are the differences between Smart, Full & Normal downloads?
Thank you for an excellent program.
Nico Morison
London & India
Map at bottom:
http://photos.theflowerraj.org/v/places/himachal_pradesh/2012/vash_shanag/
(Wish Gallery made the photo-points clickable, but the map is nice).